Refractory Brick
Refractory bricks are specialized building materials designed to withstand extremely high temperatures, thermal shock, and harsh chemical environments. Unlike regular bricks, they are engineered for applications involving intense heat, such as in furnaces, kilns, and incinerators.
Zhongke Da Refractory is a leading refractory brick manufacturer in China, offering fire clay bricks, high alumina bricks, insulating bricks and custom refractory solutions for global industries like steel, cement, and glass. OEM & ODM available.

Types of Refractory Bricks | Manufacturer & Supplier
Classification of Refractory Bricks by Material,explore Different Types of Refractory Bricks Based on Their Raw Material Composition.
Feature:
•Good thermal shock resistance
•Excellent workability
•Economical and widely used
Typical applications:
•Low temperature industrial equipment:🔥Boiler lining | 🏭Flue masonry | � Ceramic kilns(low temperature zones)
•Civil Use:🏠Household fireplaces | 🍖Commercial BBQ ovens | 🏗️Chimney linings
2. High Alumina Bricks
Feature:
•High refractoriness (up to 1700°C)
•Superior resistance to slag and corrosion
•Higher strength than fire clay bricks
Typical applications:
•High-Temperature Industrial Equipment:🔥Blast furnace linings |🏭Steel ladle slag zones |🏗️ Cement rotary kilns (burning zones)
•Specialized Uses: 🧪Glass tank furnaces | ⚡Petrochemical reactors
3.Silica Bricks
Main Composition:More than 93% SiO₂
Feature:
•Excellent resistance to acid slags
•Strong performance at high temperatures
•Limited thermal shock resistance
Typical applications:
•Acidic High-Temperature Equipment:🏭Glass furnace tank walls | 🔥Coke oven carbonization chambers | 🏗️ Hot blast stove high-temperature zones
•Special Environments:⚡ Acidic gas incinerators | 🧪 Quartz glass melting furnaces
4.Magnesia Bricks
Main Composition:More than 90% MgO
Feature:
•Excellent alkali resistance
•High melting point (up to 2000°C)
•Suitable for basic slag environments
Typical applications:
•Steel Industry:🔥Basic oxygen furnace linings | ⚡Electric arc furnace slag lines | 🏗️️ Ladle slag zones
•Non-Ferrous Metallurgy:🧪Copper/Nickel refining furnaces | ⚗️ Lead/Zinc smelting reactors
•Cement Industry:🏭Rotary kiln transition zones (alkali-rich conditions)
5.Corundum Bricks
Main Composition: ≥90% Al₂O₃ (typically made from fused alumina or sintered alumina)
Features:
•Ultra-high refractoriness (up to 1800°C)
•Excellent chemical resistance (acid and alkali slags)
•Exceptional mechanical strength and wear resistance
•Low porosity & high thermal stability
Typical Applications:
🏭Glass furnaces | 🧬Petrochemical reactors | ⚫Carbon black kilns | 🛠️Steel industry (tapholes, nozzles) | ♻️Waste incinerators | 🧱Cement and lime kilns
6.Mullite Brick
Main Composition: 65–75% Al₂O₃ with mullite phase (3Al₂O₃·2SiO₂)
Features:
•High refractoriness (up to 1750°C)
•Excellent thermal shock resistance
•Low thermal expansion and high structural stability
•Good resistance to slag and chemical attack
Typical Applications:
🧪Petrochemical furnaces | 🏭Hot blast stoves & regenerative chambers | 🔩Ceramic & metallurgical kilns | ♻️ Incinerators and kiln linings
7.Acid Proof Bricks
Main Composition:High-silica clay, shale or quartz
Feature:
•Excellent acid and chemical resistance (except hydrofluoric acid)
•Low water absorption rate
•High mechanical strength and dense structure
•Long service life in aggressive chemical environments
Typical applications:
🏭Acid storage tanks and pickling tanks | 🧬Chemical plants and reaction vessels | 🔧Flue gas ducts and scrubbers | ♻️Wastewater treatment plants | 🧯Chimneys and drain linings
8.Magnesia Carbon Bricks
Features:
•Outstanding thermal shock resistance
•High resistance to slag penetration and erosion
•Good thermal conductivity and low wettability to slag
•Non-wettability to molten steel and high-temperature stability
Typical Applications:
🧲Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) linings | 🔩Converter (BOF) linings and taphole bricks | 🧪Ladle slag lines and impact zones |🧯Steelmaking tundishes and bottom blocks
Refractory Bricks by Shape
We offer a wide range of standard and customized refractory brick shapes to meet the structural requirements of various industrial furnace linings.
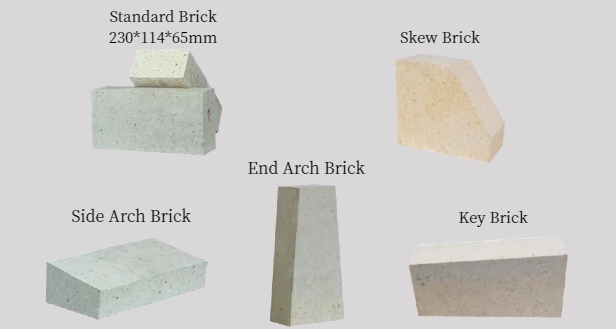
1. Standard Shapes
•Straight Bricks (Rectangular)
Dimensions: Typically 9" x 4.5" x 2.5" (230 mm x 114 mm x 64 mm) or similar ratios.
Features: Uniform edges and flat surfaces.
Applications: General furnace linings, walls, and floors.
•Arch Bricks (Tapered/Wedge)
Shapes: Radial (curved) or tapered (wedge-shaped).
Features: Designed to form arches or domes without cutting.
Applications: Roofs of kilns, rotary furnaces, and ladles.
•Radial Bricks: Curved to match furnace radius.
•Wedge Bricks: Tapered sides for tight fitting in arches.
•Skew Bricks
Shape: Angled edges (e.g., 30°, 45°, 60°) for fitting corners or complex geometries.
Applications: Corners, transitions between walls and arches.
2. Special Shapes
•Keyed Bricks
Features: Grooves, tongues, or interlocking edges.
Purpose: Improve structural stability and reduce joint gaps.
Applications: Blast furnaces, coke ovens.
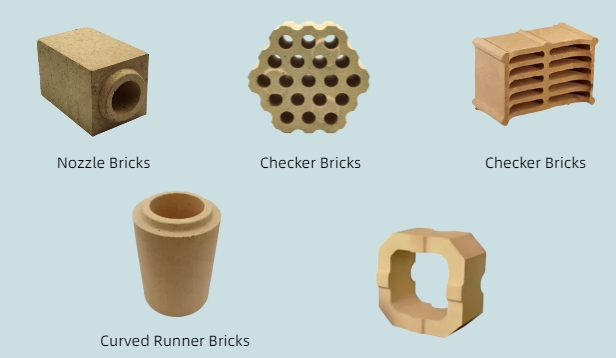
•Checker Bricks
Shape: Perforated with holes or channels.
Purpose: Maximize surface area for heat exchange.
Applications: Regenerators in glass tanks and blast furnaces.
•Nozzle Bricks
Shape: Cylindrical or conical with a central bore.
Purpose: Control flow of molten metal, slag, or gas.
Applications: Ladle nozzles, tundish outlets in steelmaking.
•Tundish Bricks
Shape: Curved or trapezoidal to line tundishes.
Applications: Continuous casting in steel plants.
•Soap Bricks
Shape: Small, rectangular (e.g., 6" x 3" x 1.5").
Purpose: Fill gaps or repair linings.
Applications: Patchwork in furnaces or kilns.
3.Custom Shapes
Tailor-made for unique industrial equipment. Examples include:
•Burner Blocks: Complex shapes with drilled holes for burner nozzles.
•Crucibles: Cylindrical or conical vessels for melting metals.
•Specialty Liners: Designed for reactors, incinerators, or chemical tanks.
Refractory Bricks By Function
The functional classification of refractory bricks is typically based on their specific applications and performance characteristics in high-temperature environments. This classification is closely related to their material composition, structural design, and intended usage scenarios.
1.High Temperature Refractory Bricks
Functional Characteristics:Designed for extreme temperatures, these bricks maintain structural stability and chemical inertness under severe thermal conditions.
Typical Materials:
•Corundum Bricks (Al₂O₃ ≥ 90%) | •Zirconia-Corundum Bricks (Al₂O₃ + ZrO₂)
•Magnesia Bricks (MgO ≥ 85%) | • Magnesia-Chrome Bricks (MgO + Cr₂O₃)
Application Scenarios:
•Steel Industry: Ladle linings, electric arc furnace linings
•Glass Melting Furnaces: Melting pools, throat and channel blocks
•Petrochemical Industry: Cracking furnaces, reforming units
Key Properties:
Refractoriness above 1800°C | Excellent high-temperature creep resistance
2.Slag-Resistant Refractory Bricks
Functional Features:Designed to resist erosion caused by molten metals, slags, or chemically corrosive media. They are typically categorized into two types: acidic slag resistance and basic slag resistance.
Acidic Slag-Resistant Bricks:
•Materials: Silica bricks (SiO₂ > 93%), fireclay bricks (Al₂O₃ + SiO₂).
•Applications: Coke ovens, glass furnaces operating in acidic environments.
Basic Slag-Resistant Bricks:
•Materials: Magnesia bricks, magnesia-carbon bricks (MgO + graphite), dolomite bricks (CaO + MgO).
•Applications: Steelmaking converters, slag lines of ladles.
Key Properties:
Low porosity | High density | Chemical compatibility with specific slags
3.Insulating Refractory Bricks (Lightweight Refractory Bricks)
Functional Features:Characterized by low thermal conductivity, these bricks are designed to reduce heat loss while still offering a certain degree of refractoriness.
Typical Materials:
•Lightweight fireclay bricks, diatomite bricks, alumina hollow ball bricks
•Ceramic fiber bricks (unsintered, flexible)
Application Scenarios:
•Insulating layers in industrial kilns and furnaces
•Linings for thermal pipelines
•Heat insulation shells for high-temperature equipment
Key Properties:
•High porosity (60%–85%) | •Low bulk density (0.6–1.5 g/cm³) | •Typical working temperature ≤ 1300°C (some materials can withstand up to 1600°C)
4.Wear-Resistant Refractory Bricks
Functional Features:Designed to withstand abrasion caused by high-velocity gas flow, particulate materials, or mechanical friction.
Typical Materials:
•High alumina bricks (Al₂O₃ 60%–75%)
•Silicon carbide bricks (SiC + clay)
•Corundum–silicon carbide composite bricks
Application Scenarios:
•Preheaters and grate coolers in cement kilns
•Linings of circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers
•Troughs in blast furnaces (areas exposed to molten iron erosion)
Key Properties:
High hardness (Mohs hardness ≥ 8) | Compressive strength > 50 MPa
5.Thermal Shock-Resistant Refractory Bricks
Functional Features:Engineered to withstand rapid temperature changes (thermal shock) without cracking or spalling.
Typical Materials:
•Mullite bricks (3Al₂O₃·2SiO₂)
•Zircon bricks (ZrSiO₄)
•Andalusite bricks, cordierite bricks (low thermal expansion)
Application Scenarios:
•Ceramic roller kilns
•Doors of heat treatment furnaces
•Checker bricks in the regenerator chambers of glass furnaces
Key Properties:
•Low thermal expansion coefficient (< 5×10⁻⁶/°C)
•High thermal shock resistance (> 30 cycles at 1100°C ↔ water quench)
6.Functional Composite Refractory Bricks
Functional Features:These bricks integrate multiple functionalities such as electrical conductivity, anti-permeability, and catalytic activity to meet the demands of specialized high-temperature environments.
Typical Types:
•Conductive Refractory Bricks: e.g., magnesia-carbon bricks used as anodes in DC electric arc furnaces
•Anti-Penetration Bricks: incorporating zircon or spinel to prevent molten metal infiltration
•Catalytic Refractory Bricks: loaded with catalysts for exhaust gas treatment
Application Scenarios:
•Specialized metallurgical furnaces
•Environmental protection equipment
•Electrolytic cells and high-temperature reaction systems
7.Precast Refractory Bricks (Shaped Functional Bricks)
Functional Features:These bricks are preformed according to the specific shapes of industrial equipment, minimizing on-site joints and enhancing structural integrity.
Typical Types:
•Burner bricks, peep sight bricks, anchor bricks
•Monolithic precast blocks (e.g., ladle seating blocks)
Key Advantages:
•High installation efficiency
•Excellent spalling resistance
•Extended service life by 20%–30%
Refractory Bricks by Industry Application
Refractory bricks can be classified based on their specific installation positions and working environments within industrial equipment. Each area requires bricks with tailored performance to withstand high temperatures, mechanical stress, and chemical attack.
🧲Steelmaking
For: Electric arc furnaces, ladles, converters
Recommended:Magnesia carbon bricks | High alumina bricks | Alumina carbon bricks
🧱Cement Industry
For: Rotary kilns, preheaters, clinker coolers
Recommended:Anti-stripping high alumina bricks | Spinel bricks | Fireclay bricks
🔍Glass Industry
For: Melting tanks, regenerators, throats
Recommended:AZS bricks | Zircon bricks | Silica bricks
♨️Coking & CDQ (Coke Dry Quenching)
For: Coke ovens, CDQ chambers, flue walls
Recommended:Silica bricks | Fireclay bricks | High alumina bricks
⚫Carbon Industry
For: Baking furnaces, calcination kilns
Recommended:Mullite bricks |High alumina bricks|Anti-oxidation fireclay bricks
🛢️Petrochemical / Chemical
For: Cracking furnaces, reformers
Recommended:High alumina bricks | Lightweight insulating bricks | Mullite bricks





 Zhengzhou Zhongkeda Refractory Materials Co., Ltd
Zhengzhou Zhongkeda Refractory Materials Co., Ltd

